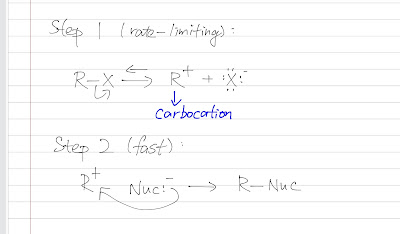Factors affecting rate of SN1
The reactivity of a SN1 reaction is determined by 3 factors: 1. the substituent 2. leaving group 3. solvent effect Note that the nucleophilicity is not considered here but a weak nucleophile is usually preferred. Substituent Substituent is the things that attached to the carbocation. As the carbocation formation is rate-determining step, a stable carbocation is necessary. A carbocation is positively charged and it is electron deficient. So it needs some groups/ substituents that are electron-donating. Methyl group (not hydrogen anymore) stabilizes the carbonation by the inductive effect (donating electrons through the sigma bond) hyperconjucation (donating electrons through the overlap of the sp3 orbital and the empty p orbital) Therefore, a more substituted alkyl halide is more favored than a primary alkyl halide, which is the opposite of the SN2 reaction. Resonance (typically double bond or oxygen lone pair e-) also stabilized the carbocation. Leaving Group ...